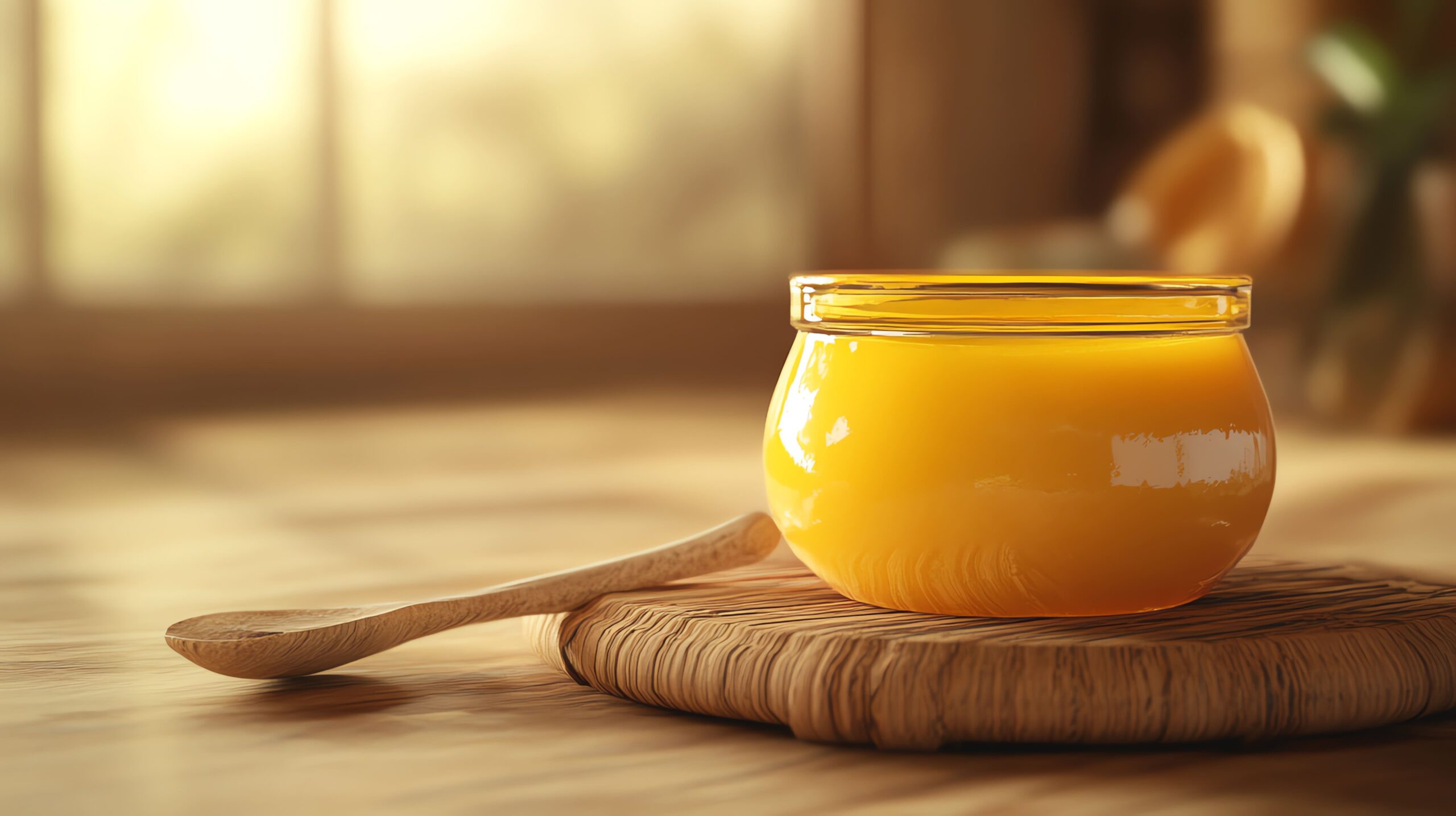
Ghee has been a staple in Indian kitchens for centuries, renowned for its rich flavor, aroma, and culinary versatility. However, not all ghee is created equal. In recent years, the rise of A2 Desi Cow Ghee has sparked interest among health enthusiasts and culinary experts alike. But what exactly sets A2 Desi Cow Ghee apart from regular ghee? In this blog, we’ll delve into the origins, health benefits, production processes, and nutritional profiles of A2 Desi Cow Ghee and regular ghee to help you understand the differences and make informed choices for your health and cooking needs.
Understanding Ghee
Before diving into the comparison, it’s essential to understand what ghee is. Ghee is a type of clarified butter that is made by simmering butter to remove moisture and milk solids, leaving behind a golden, nutty-flavored fat. It is a popular cooking medium in Indian cuisine and has been used in Ayurvedic medicine for its numerous health benefits.
The Origins of A2 Desi Cow Ghee
The term “A2” refers to the type of beta-casein protein found in the milk of certain cows. A2 cows, predominantly indigenous breeds like the Gir, Sahiwal, and Red Sindhi, produce milk containing the A2 beta-casein protein, which is believed to be easier to digest and less likely to cause inflammation compared to A1 beta-casein, found in the milk of many European breeds like Holstein and Jersey cows.
The traditional practices of milking and using these indigenous cows have been a part of Indian culture for generations, making A2 Desi Cow Ghee a product rooted in history and tradition.
1. The Production Process
The production of A2 Desi Cow Ghee is steeped in traditional methods. Here’s a breakdown of how A2 Desi Cow Ghee is made compared to regular ghee:
a. Milk Source:
A2 Desi Cow Ghee: Made from the milk of A2 cow breeds. The milk is typically sourced from small-scale, local farms that practice traditional, ethical farming.
Regular Ghee: Can be made from the milk of A1 or A2 cows, but often comes from commercial dairy farms that may prioritize yield over quality.
b. Milk Processing:
A2 Desi Cow Ghee: The milk is usually collected fresh and is often raw or minimally processed. It is then cultured to promote fermentation before churning to separate butter from buttermilk.
Regular Ghee: The milk may undergo pasteurization and other processes that strip some of its nutrients. It is often churned to separate butter from buttermilk, but the starting milk quality may vary.
2. Clarification:
A2 Desi Cow Ghee: The butter is simmered slowly over low heat, allowing the natural flavors to develop and impurities to be removed.
Regular Ghee: While it can also be clarified similarly, mass-produced regular ghee may use faster methods that affect flavor and quality.
Nutritional Comparison
Understanding the nutritional differences between A2 Desi Cow Ghee and regular ghee can provide insight into why many health-conscious individuals prefer A2 ghee.
1. Protein Content:
A2 Desi Cow Ghee: Contains A2 beta-casein, which is considered easier to digest and may lead to fewer digestive issues and allergic reactions. Many people who are lactose intolerant can tolerate A2 milk and ghee better.
Regular Ghee: Contains both A1 and A2 proteins, which may cause digestive discomfort in some individuals, especially those sensitive to A1 beta-casein.
2. Fat Composition:
Both A2 Desi Cow Ghee and regular ghee are high in healthy saturated fats, but A2 ghee is believed to have a better balance of fatty acids.
A2 ghee is rich in short-chain and medium-chain fatty acids, which are beneficial for heart health and energy metabolism.
3. Vitamins and Antioxidants:
A2 Desi Cow Ghee: Known for being rich in fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K. It also contains antioxidants that contribute to overall health.
Regular Ghee: While it also contains these vitamins, the quality and concentration may vary depending on the milk source and processing methods.
Health Benefits
Both A2 Desi Cow Ghee and regular ghee offer health benefits, but the unique qualities of A2 ghee provide some additional advantages:
1. Digestive Health:
A2 Desi Cow Ghee: Its A2 protein content is easier on the digestive system, making it suitable for individuals with lactose intolerance or dairy sensitivities.
Regular Ghee: May lead to digestive discomfort for those sensitive to A1 beta-casein.
2. Anti-inflammatory Properties:
A2 Desi Cow Ghee: Contains butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid that has been shown to reduce inflammation and promote gut health.
Regular Ghee: Also contains butyrate but may not have the same anti-inflammatory benefits due to the presence of A1 protein.
3. Nutrient Absorption:
A2 Desi Cow Ghee: Enhances the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and minerals from other foods, making it an excellent addition to meals.
Regular Ghee: Provides similar benefits, but the nutrient absorption may vary based on the quality of the ghee.
4. Weight Management:
Both A2 Desi Cow Ghee and regular ghee can support weight management due to their satiating nature, but A2 ghee’s unique fatty acid profile may offer additional metabolic benefits.
Culinary Uses
Ghee is celebrated for its high smoke point, making it an excellent cooking oil for frying, sautéing, and baking. Both A2 Desi Cow Ghee and regular ghee can be used interchangeably in recipes, but the flavor and aroma can differ significantly:
- A2 Desi Cow Ghee: Offers a rich, nutty flavor that enhances the taste of dishes. It is especially favored in traditional Indian recipes and can elevate the flavor of desserts, curries, and roasted vegetables.
- Regular Ghee: The flavor can be milder and less pronounced, making it a versatile cooking fat but sometimes lacking the depth of taste found in A2 ghee.
Environmental and Ethical Considerations
The production of A2 Desi Cow Ghee often aligns with sustainable and ethical farming practices. Many A2 cow farmers prioritize the welfare of their animals and the health of the land. In contrast, regular ghee may be sourced from large-scale dairy operations that may not prioritize sustainability or animal welfare.
When choosing between A2 Desi Cow Ghee and regular ghee, it’s essential to consider not only the health benefits but also the environmental impact and ethical considerations of your food sources.
Conclusion
In summary, A2 Desi Cow Ghee and regular ghee offer unique benefits and flavors, with A2 ghee standing out for its digestibility, nutrient profile, and connection to traditional farming practices. While both types of ghee can be enjoyed in your kitchen, A2 Desi Cow Ghee may be the preferred choice for those seeking a healthier, more flavorful option.
Ultimately, the decision comes down to personal preference and dietary needs. As you explore the world of ghee, consider trying both types to discover the one that suits your palate and health goals best. Whether you’re using ghee for cooking, baking, or simply as a spread, the rich tradition and health benefits of this golden elixir can enhance your meals and overall well-being.
By making informed choices about the type of ghee you use, you can enjoy its many benefits while supporting ethical farming practices and nourishing your body with quality ingredients.