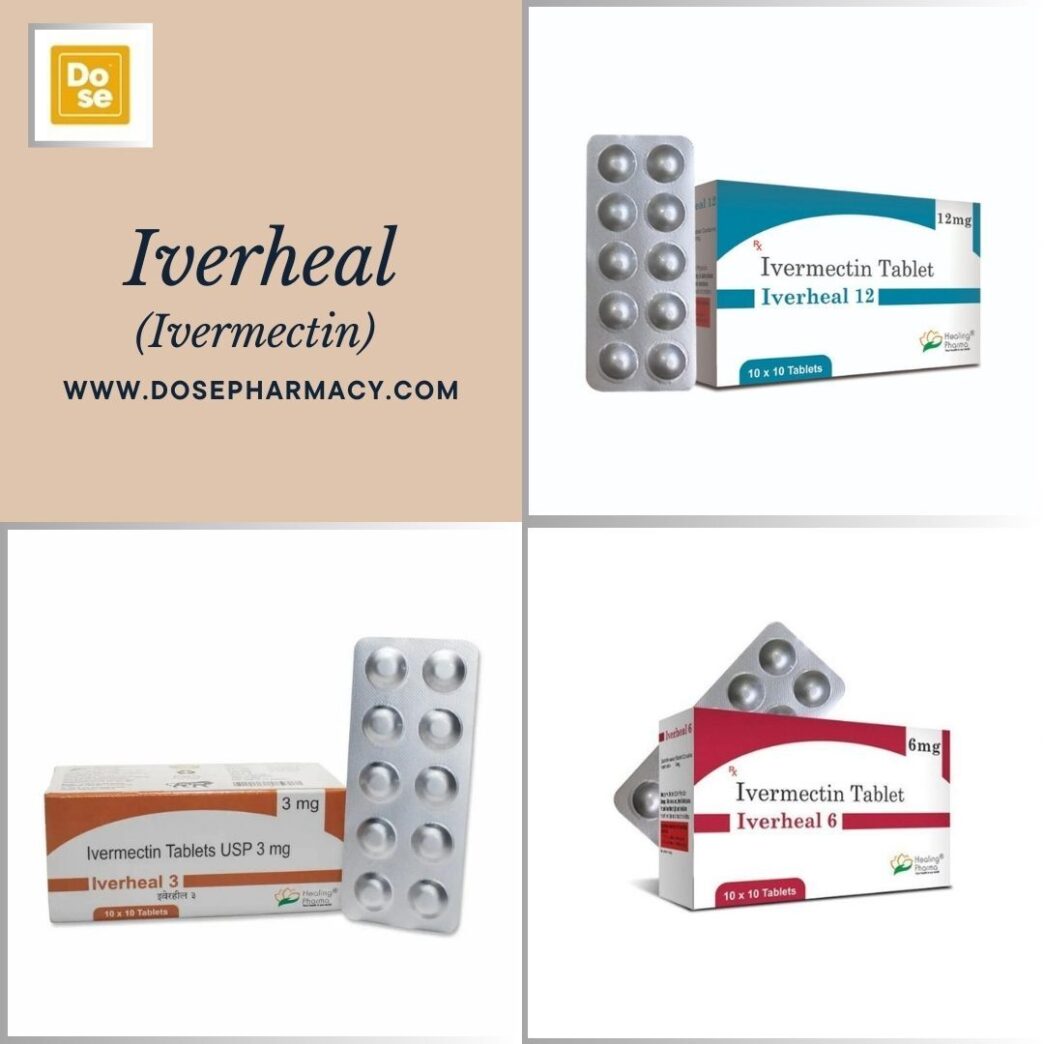
Ivermectin is a widely used antiparasitic medication that has garnered global recognition for its efficacy in treating a range of parasitic infections. Initially introduce in the late 1970s, Ivermectin has been used in both veterinary and human medicine. Over the years, it has proven its worth by effectively combating numerous parasitic diseases that plague millions worldwide, especially in regions with poor sanitation and limited access to healthcare.
This blog delves into how Ivermectin works, the parasitic infections it treats, the dosage and safety guidelines, and its impact on global health.
Understanding Ivermectin
Ivermectin is a broad-spectrum antiparasitic agent derived from avermectin, a natural compound produce by a soil bacterium, Streptomyces avermitilis. It functions by interfering with the nervous system of parasites, leading to paralysis and death. Ivermectin buy online from dosepharmacy and its mechanism is highly effective against many parasitic organisms that affect both humans and animals.
The discovery of Ivermectin revolutionized the treatment of parasitic diseases, especially in low-income regions where parasitic infections are endemic. Its wide range of applications, coupled with its affordability, makes it a cornerstone of global health efforts to control parasitic diseases.
Key Parasitic Infections Treated by Ivermectin
Ivermectin 6 mg tablet dose has been found effective against a variety of parasitic infections. Here are some of the most common conditions where Ivermectin is the treatment of choice:
1. Onchocerciasis (River Blindness)
Onchocerciasis, also known as river blindness, is caused by the parasitic worm Onchocerca volvulus, which is transmitted through the bites of blackflies. This disease is prevalent in sub-Saharan Africa and parts of South America. The parasitic worms produce larvae that move to the skin and eyes, causing severe itching, skin changes, and ultimately, blindness if untreated.
Ivermectin is an essential component of the global fight against river blindness. By killing the larvae of the parasite, it prevents the progression of the disease and reduces the spread of infection. In areas where onchocerciasis is endemic, mass drug administration (MDA) programs distribute Ivermectin regularly, significantly reducing the incidence of blindness caused by this parasitic disease.
2. Strongyloidiasis
Strongyloidiasis is cause by the intestinal parasite Strongyloides stercoralis, which can infect humans through direct contact with contaminated soil. The parasite can cause a wide range of symptoms, from mild gastrointestinal issues to life-threatening hyperinfection, particularly in people with weakened immune systems.
Ivermectin is the drug of choice for treating strongyloidiasis. It works by paralyzing and killing the parasite, helping to eliminate the infection from the intestines. For immunocompromised patients, Ivermectin has been particularly life-saving, as strongyloidiasis can become severe and difficult to treat in such cases.
3. Lymphatic Filariasis
Lymphatic filariasis, commonly known as elephantiasis, is cause by infection with Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi, or Brugia timori, all of which are transmit through mosquito bites. These parasites infect the lymphatic system, leading to severe swelling, disability, and social stigma due to the grotesque physical disfigurement it causes.
Ivermectin, in combination with other antiparasitic drugs like albendazole, is use to reduce the spread of lymphatic filariasis by targeting the microfilariae (larval stage of the parasite) in the blood. Over time, mass treatment programs have significantly reduced the burden of this debilitating disease in many countries.
4. Scabies and Head Lice
While primarily use to treat parasitic worms, Ivermectin is also effective against ectoparasites such as scabies mites and head lice. Scabies is a skin condition caused by Sarcoptes scabiei, which burrows into the skin and causes intense itching and rashes. Head lice are tiny insects that infest the scalp and feed on blood, causing itching and irritation.
Topical and oral Ivermectin can be use to treat both scabies and head lice, providing relief from these uncomfortable and contagious conditions. For people living in crowded environments like schools or refugee camps, where outbreaks of scabies and lice are common, Ivermectin offers an efficient solution to control and prevent their spread.
5. Other Parasitic Infections
In addition to the conditions mentioned above, Ivermectin has shown effectiveness in treating other parasitic infections, such as ascariasis (roundworm infection), trichuriasis (whipworm infection), and cutaneous larva migrans (caused by hookworm larvae). Its broad-spectrum action against various parasitic organisms has made it an invaluable resource in the treatment of parasitic diseases.
Dosage and Administration
The dosage of Ivermectin varies depending on the parasitic infection being treat and the patient’s weight. Typically, Ivermectin is administer orally as a single dose or a short course of doses. For instance, in the treatment of onchocerciasis, Ivermectin is give every 6 to 12 months to reduce the risk of reinfection.
For scabies and head lice, both oral and topical forms of Ivermectin are available, with the oral form often given as a single dose followed by a second dose a week later to ensure all parasites are kill.
It’s essential to follow the prescribed dosage regimen and not self-medicate, as improper use of Ivermectin can lead to suboptimal results or adverse reactions.
Safety and Side Effects
Ivermectin is generally well-tolerate when use at recommend doses. Most side effects are mild and transient, including dizziness, nausea, diarrhea, and skin rashes. In the treatment of onchocerciasis, some patients may experience an inflammatory reaction called the Mazzotti reaction, which occurs as the body responds to the death of large numbers of parasites. Symptoms include fever, swelling, joint pain, and itching.
People with a history of liver disease or who are taking certain medications should consult a healthcare provider before using Ivermectin to ensure there are no interactions or contraindications.
Ivermectin’s Role in Global Health
Ivermectin has played a pivotal role in the global effort to control and eliminate parasitic diseases, particularly in resource-limited settings. Through initiatives like the World Health Organization’s (WHO) programs to control river blindness and lymphatic filariasis, Ivermectin has distribute to millions of people in affect regions, significantly reducing the prevalence of these diseases.
In many regions, mass drug administration (MDA) campaigns that distribute Ivermectin regularly have not only treated existing infections but also prevented new infections, leading to a decline in disease transmission. These efforts have been instrumental in improving the quality of life for millions and achieving progress toward eliminating these diseases.
Conclusion
Ivermectin remains a crucial weapon in the fight against parasitic infections. Its effectiveness in treating a wide range of parasitic diseases, from onchocerciasis to scabies, has saved countless lives and reduced the suffering caused by these debilitating conditions. With proper use and continued global efforts, Ivermectin can help to further reduce the burden of parasitic diseases, especially in regions where these infections are endemic.
For individuals suffering from parasitic infections, consulting a healthcare provider and adhering to prescribed treatments are essential steps to recovery and preventing the spread of these diseases.