The rapid advancement of technology has brought significant changes across industries, with Industrial IoT (IIoT) and automation leading the charge. Among the critical components driving this transformation are smart valves, which are increasingly becoming indispensable for optimizing industrial processes. These intelligent devices offer real-time data insights, remote control capabilities, and seamless integration with automated systems. This article explores the evolution, benefits, and future potential of smart valves in industrial IoT and automation.
Understanding Smart Valves and Their Role in IIoT
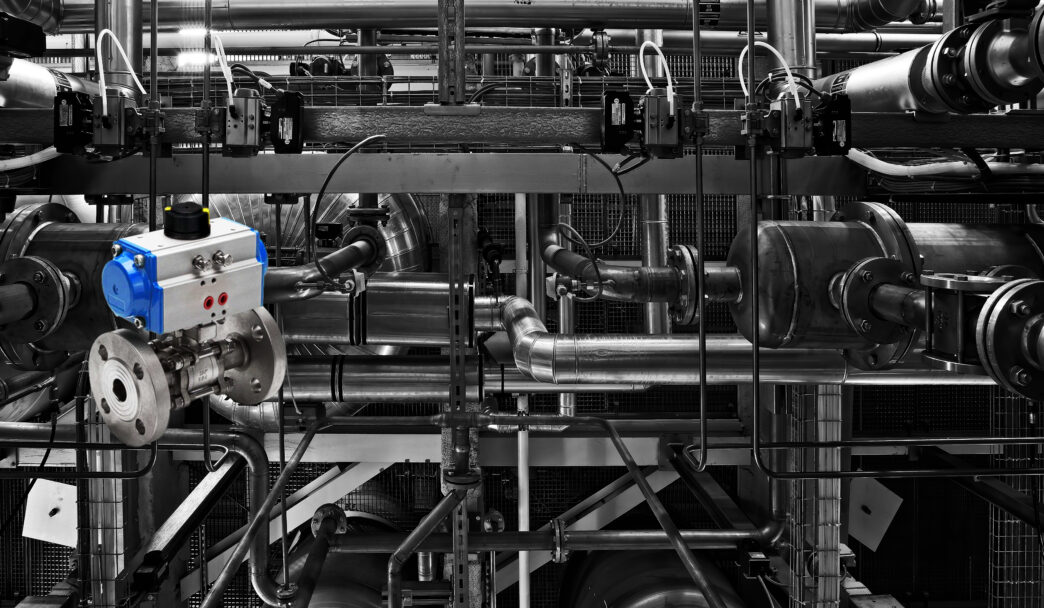
Smart valves are equipped with sensors, actuators, and communication modules that enable them to monitor and control fluid flow efficiently. Unlike traditional valves, which require manual intervention, smart valves provide real-time feedback on parameters such as pressure, temperature, and flow rate. They communicate this data to centralized systems or cloud platforms via protocols like MQTT, Modbus, or OPC UA, enabling advanced analytics and decision-making.
Key Features of Smart Valves
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Operators can monitor valve performance and make adjustments remotely, reducing the need for on-site inspections.
- Predictive Maintenance: Sensors detect anomalies or early signs of wear, enabling proactive maintenance before issues escalate.
- Integration with Automation Systems: Smart valves can be integrated into SCADA, DCS, and other industrial automation frameworks.
- Self-Diagnostics: They perform continuous self-assessments, ensuring optimal performance and alerting operators of potential failures.
- Energy Efficiency: By optimizing fluid control, smart valves contribute to reduced energy consumption and improved system efficiency.
Benefits of Smart Valves in Industrial Automation
- Enhanced Process Efficiency
Smart valves ensure precise control of fluid dynamics, minimizing wastage and maximizing productivity. In industries such as chemical processing and oil & gas, where accuracy is paramount, smart valves play a crucial role in maintaining product quality and process efficiency. - Improved Safety and Compliance
Safety is a top priority in industrial environments. Smart valves help prevent hazardous situations by providing early warnings of pressure surges, leaks, or equipment failures. Additionally, they support regulatory compliance by maintaining accurate records of operational data. - Cost Savings
The ability to monitor and control valves remotely reduces labor costs associated with manual inspections and maintenance. Predictive maintenance capabilities also help avoid costly downtime by addressing potential failures before they occur. - Data-Driven Decision Making
With access to real-time data, companies can make informed decisions about process adjustments, resource allocation, and maintenance schedules. Advanced analytics, powered by machine learning algorithms, further enhance decision-making by identifying patterns and predicting future trends.
Applications of Smart Valves in Different Industries
- Oil & Gas
In the oil and gas industry, smart valves are used to monitor and control the flow of crude oil, natural gas, and refined products. They play a crucial role in upstream, midstream, and downstream operations, ensuring optimal performance and minimizing environmental risks. - Water Treatment
Smart valves are integral to modern water treatment plants, where they regulate water flow and pressure, detect leaks, and monitor water quality. They contribute to efficient resource management and help address the growing global demand for clean water. - Pharmaceuticals
In pharmaceutical manufacturing, maintaining sterile and controlled environments is critical. Smart valves ensure precise control of fluids and gases, supporting high standards of hygiene and product quality. - Power Generation
Power plants rely on smart valves to control steam and coolant flows, ensuring efficient energy production and minimizing downtime. They are particularly valuable in renewable energy systems, such as solar thermal and geothermal power plants. - Food & Beverage
Smart valves help maintain hygiene and consistency in food and beverage production by enabling precise control of ingredients and cleaning processes.
Emerging Trends and Future Innovations
- AI and Machine Learning Integration
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) with smart valves is set to revolutionize industrial automation. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data collected by smart valves to optimize processes, predict failures, and enhance system performance. - 5G Connectivity
With the rollout of 5G technology, smart valves will benefit from faster and more reliable communication. This will enable real-time data transfer and enhance the performance of industrial IoT systems. - Digital Twins
Digital twin technology involves creating a virtual replica of physical assets, including smart valves. This allows companies to simulate operations, predict outcomes, and test changes without disrupting actual processes. - Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
As industries strive to reduce their carbon footprint, smart valves will play a critical role in achieving energy efficiency and sustainability goals. By optimizing resource use and minimizing emissions, they contribute to greener operations. - Edge Computing
Edge computing brings data processing closer to the source, reducing latency and improving response times. Smart valves equipped with edge computing capabilities can make instant decisions without relying on cloud-based systems.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their advantages, the adoption of smart valves comes with challenges.
- High Initial Costs: The implementation of smart valves and associated infrastructure requires significant investment.
- Cybersecurity Risks: As smart valves become connected to industrial networks, they become potential targets for cyberattacks. Robust security measures are essential to protect sensitive data and operations.
- Compatibility Issues: Integrating smart valves with existing systems can be complex, especially in industries with legacy equipment.
Conclusion
The future of smart valves in industrial IoT and automation looks promising. These devices offer unparalleled benefits in terms of efficiency, safety, and cost savings. As technologies like AI, 5G, and edge computing continue to evolve, smart valves will become even more sophisticated and integral to industrial operations. Companies that embrace this technology stand to gain a competitive edge, driving innovation and sustainability in their respective fields.